Coats
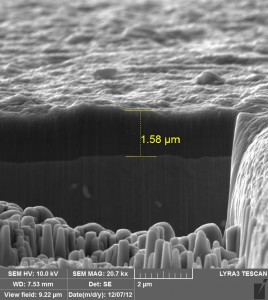
The coat is a very thin film of functional material with thickness of commonly several micrometers (most often 2-4 μm), applied at the surface of underlayer /target. The coats may be applied as liquid, gaseous or solid substances. These may be also measured and tested on thickness, hardness, adhesion, roughness, right covering, and many other characteristics.
At the present the coating is carried out using the several methods. The most used methods of applying the coats in form of solid matters include PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) and CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) coating methods.
STATON company deals with coats and coating based on PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) – the method of so called plasma cathodic vaporization or magnetron sputtering. All forms of PVD-coating are performed in the vacuum.
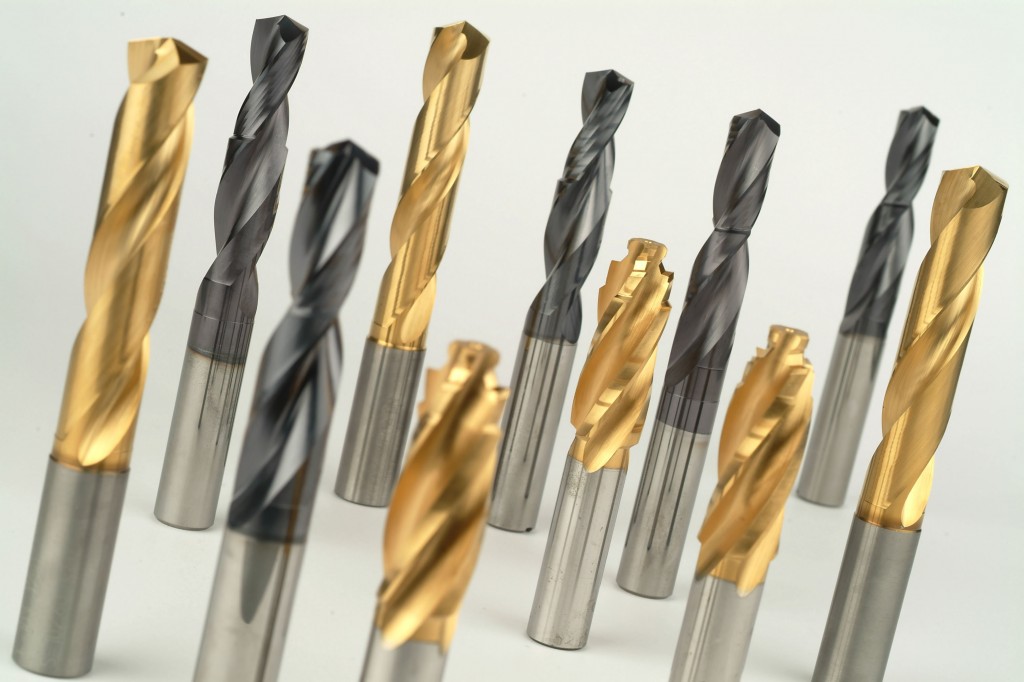
The coating centre STATON – Turany has more than 16-years tradition in applying the hard abrasion-resistant coats to the cutting tools (drills, milling cutters, plates, saws, screwing taps…) and forming tools (punches, moulds, dies, benders…).
We use for coating the newest technologies of ARC evaporation and magnetron sputtering.
The thin layers as TiN, TiCN, TiAlN, CrAlSiN, TiBN, nanocomposites and multilayer coats significantly influence the surface characteristics of tool.
Effect of coats to the tool properties:
- decreases friction coefficient
- several times increases surface hardness
- increases heat resistance of tool tip
- increases oxidizing and chemical resistance
- allows machining of hardly machinable materials
- allows increase of cutting speeds
- decreases cutting forces
- decreases roughness of machined surface
- decreases creation of built-up edge
- minimizes volume of cooling fluid and allows even dry machining
Contact
Staton s.r.o.
Sadová 1148
038 53 TURANY, Slovakia
Tel.: +421 43 4292362
Tel.: +421 43 4292638
Fax: +421 43 4292585
Staton s.r.o.
Stahlkonstruktionen
www.statonsk.eu